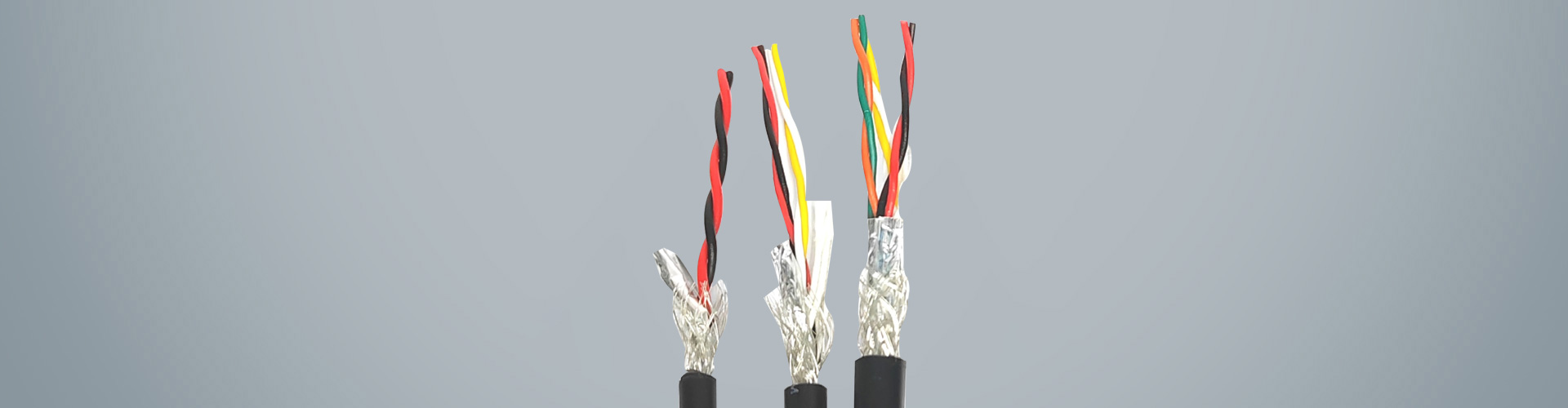
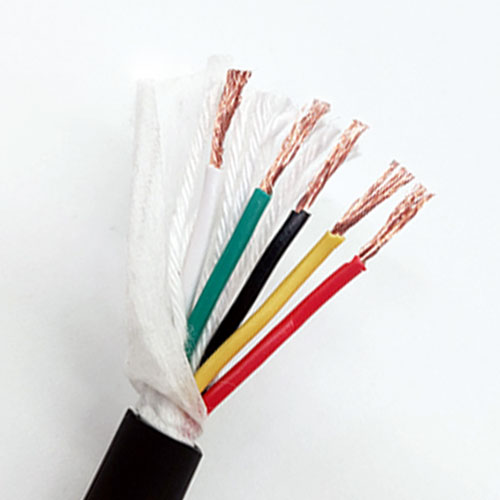
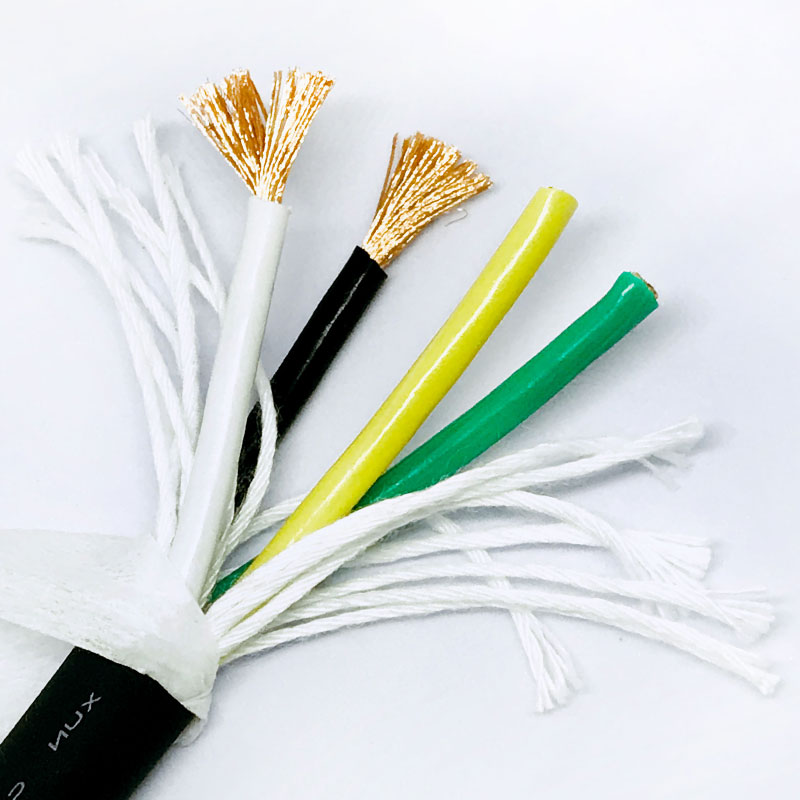
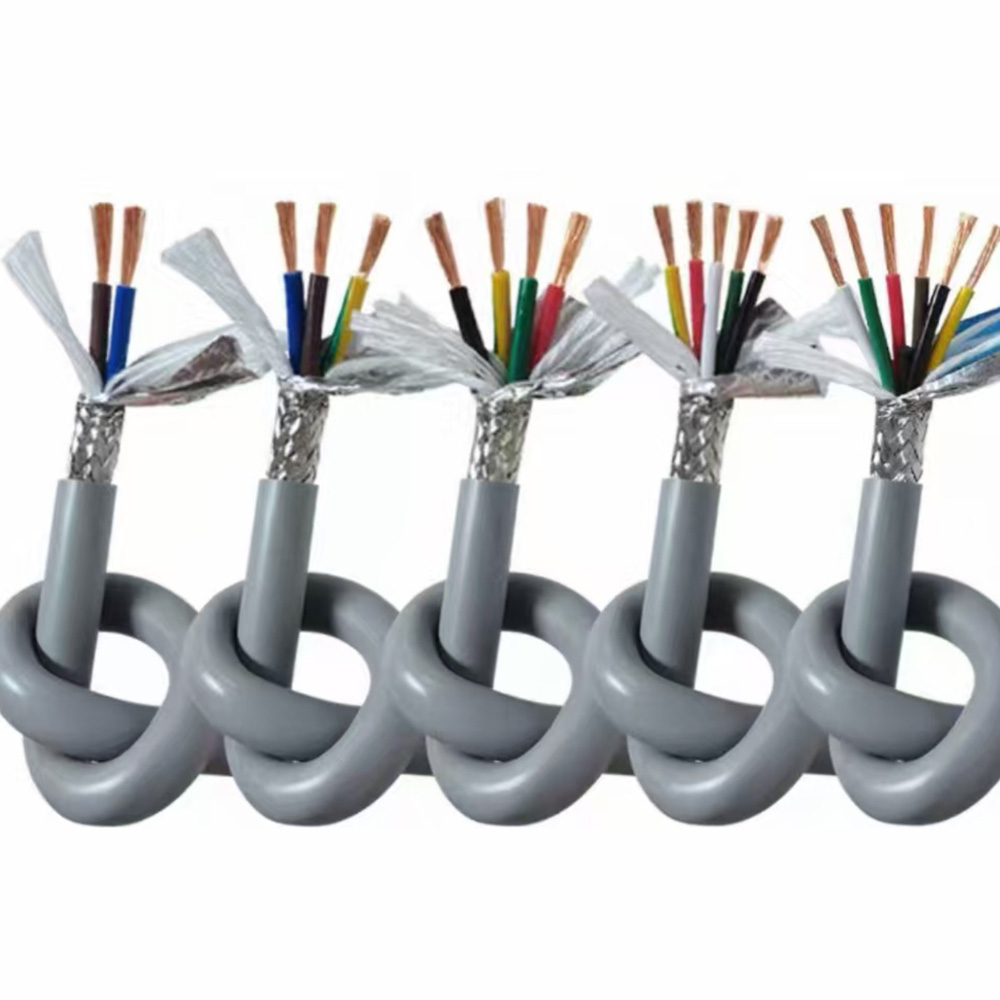
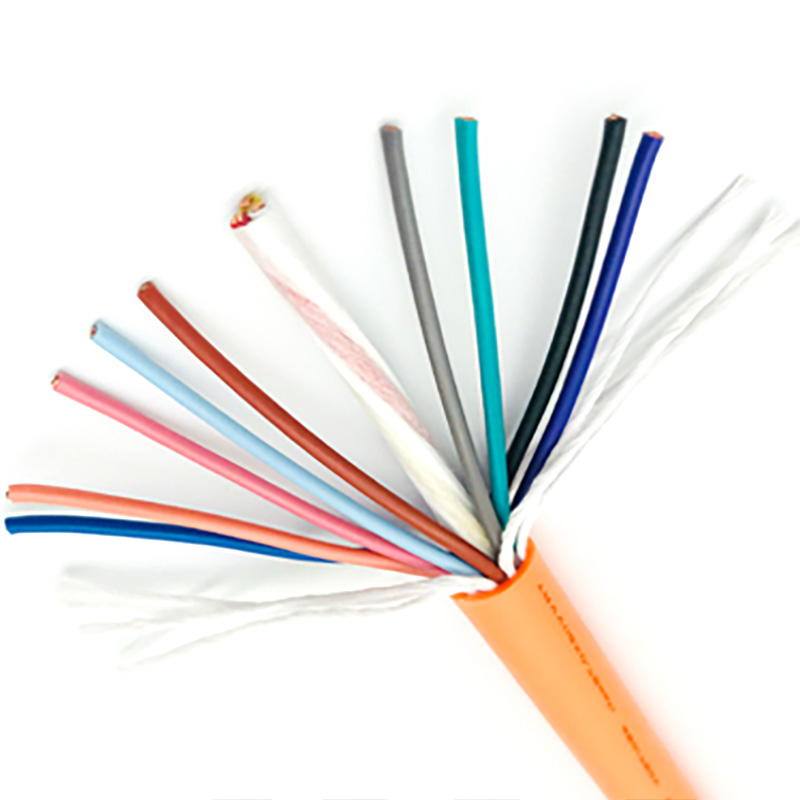
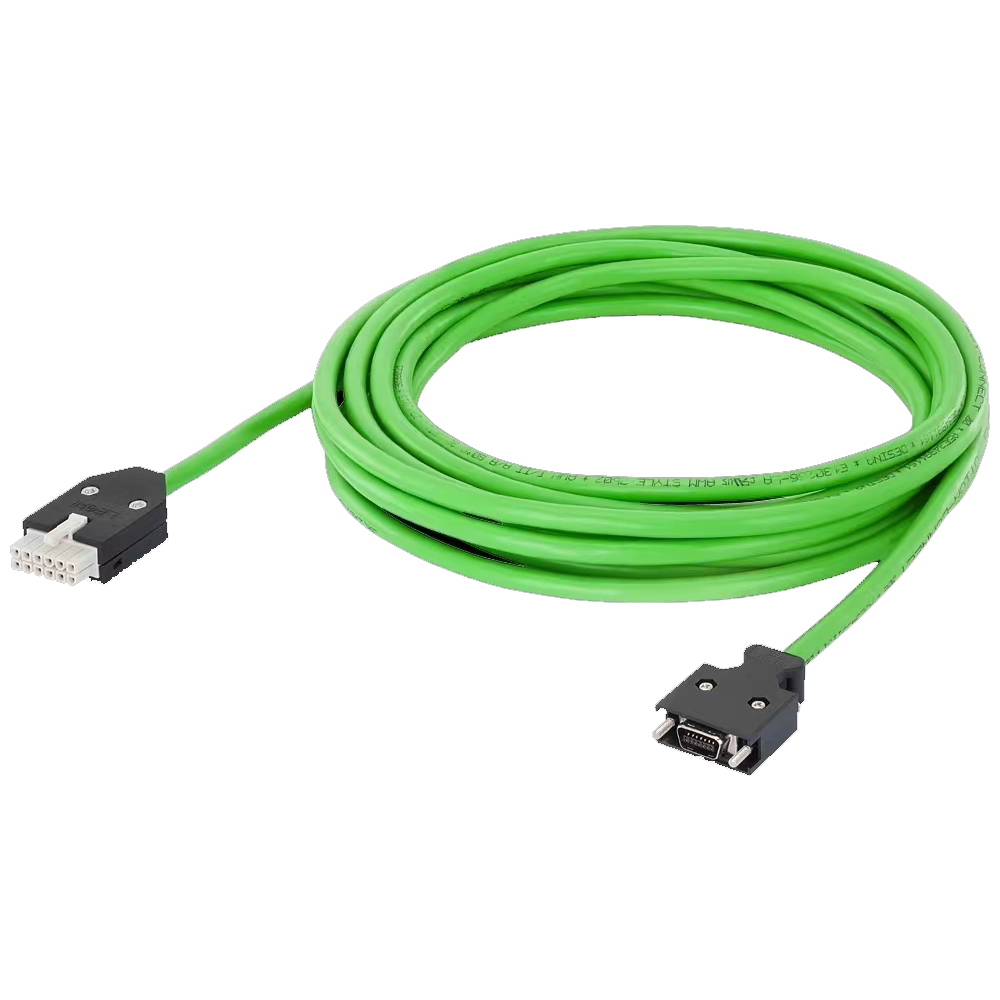
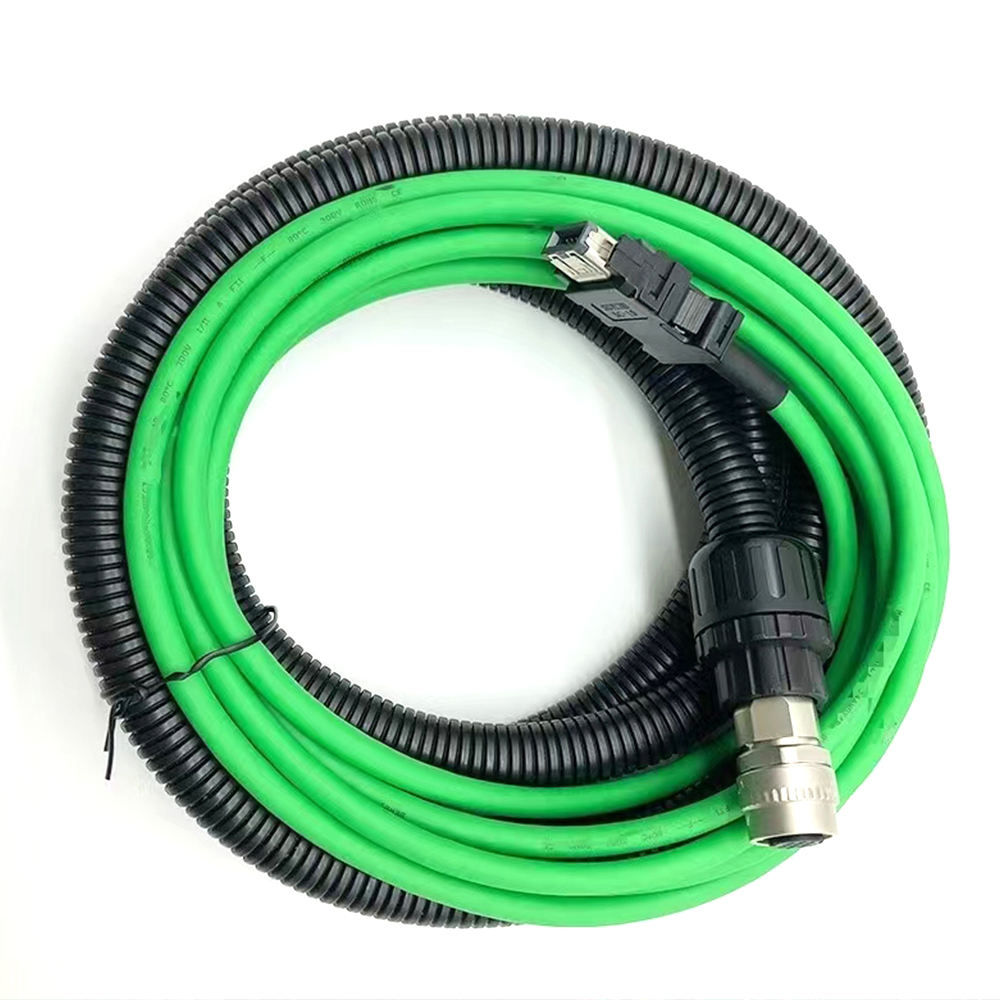
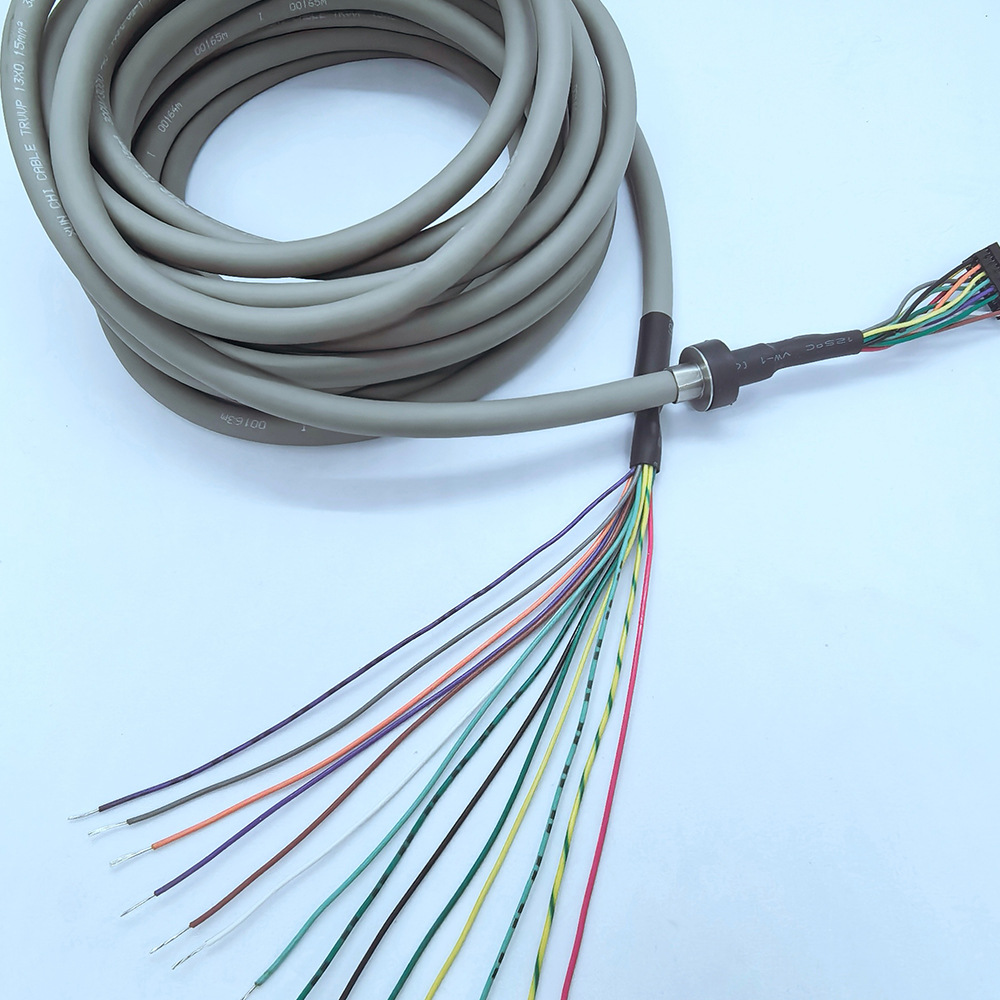
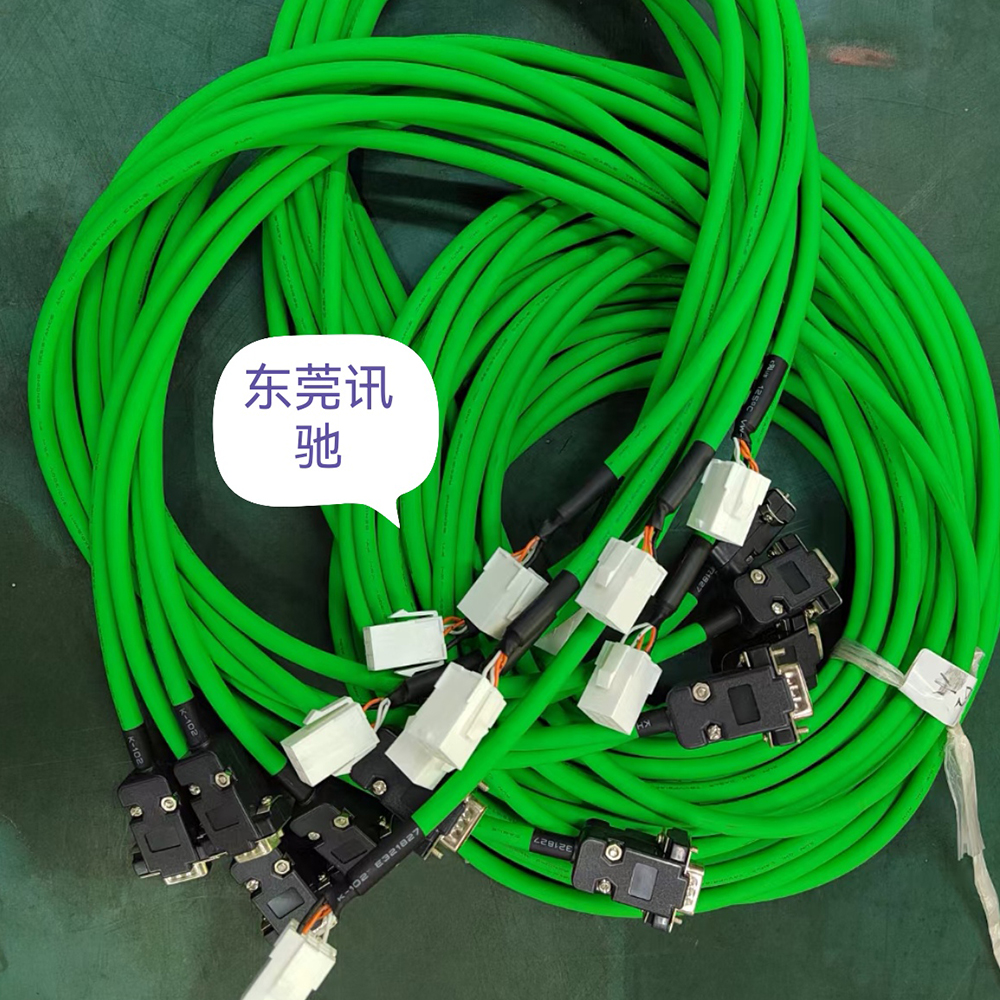
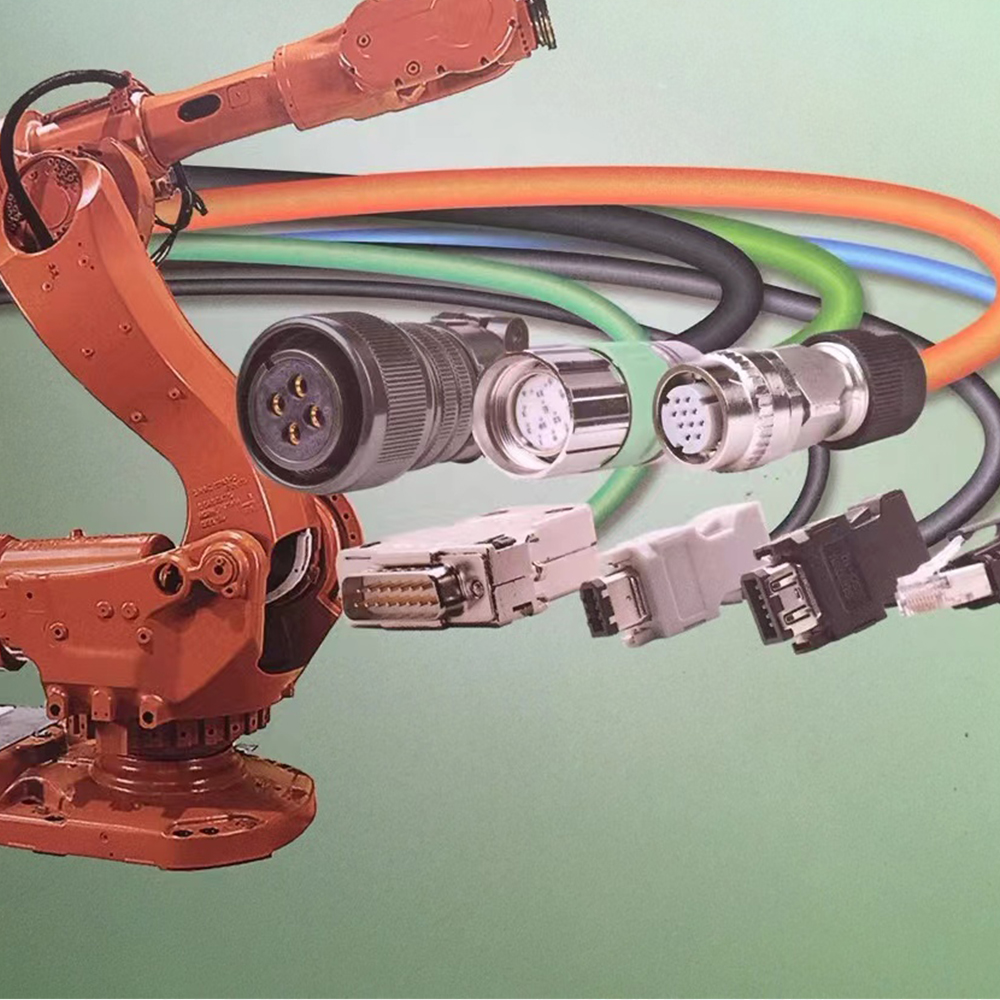
Highly Fexible Energy Chain Cable
Highly Fexible Energy Chain Cable
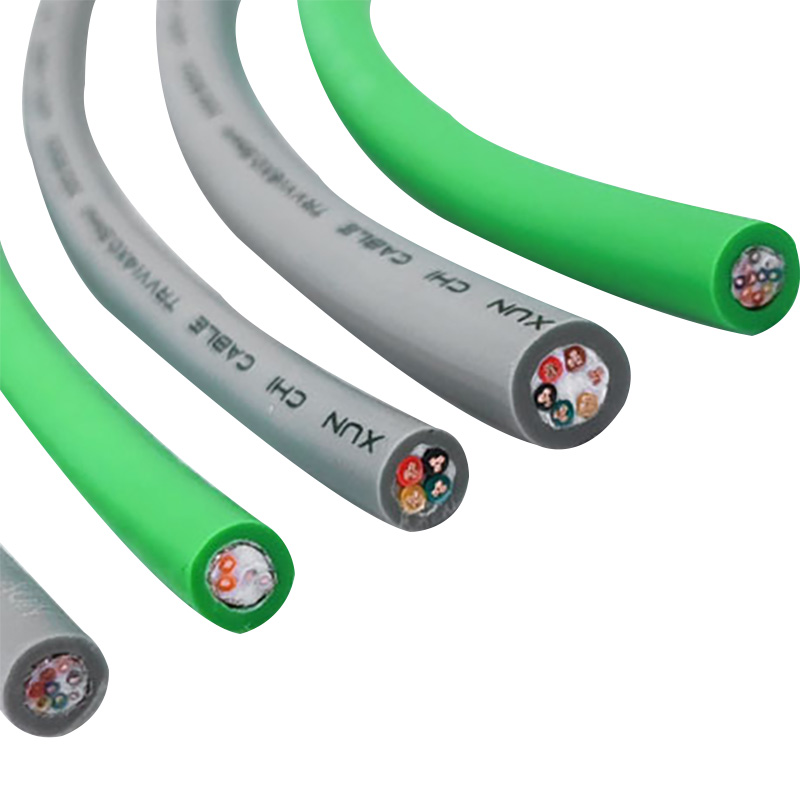
- Product Brief: Nylon chain cable, also known as nylon drag chain cable, is a specialized cable designed for use in drag chain systems, where it needs to withstand continuous motion, bending, and mechanical stress. It incorporates nylon materials in its construction, either in the cable’s structural components or as part of the protective elements, to deliver exceptional performance in dynamic industrial environments.
Description
In the fast-paced and high-precision world of modern industrial automation, the reliability of every component directly affects the overall efficiency and operational stability of the equipment. Among these critical components, the highly flexible energy chain cable stands out as an indispensable "nerve and blood vessel" for industrial machinery, playing a pivotal role in transmitting power, signals, and data in dynamic motion environments. Unlike ordinary cables that are only suitable for fixed laying, this specialized cable is engineered to withstand repeated bending, torsion, and friction, making it the first choice for equipment that requires continuous movement, such as robotics, CNC machines, and automated production lines.
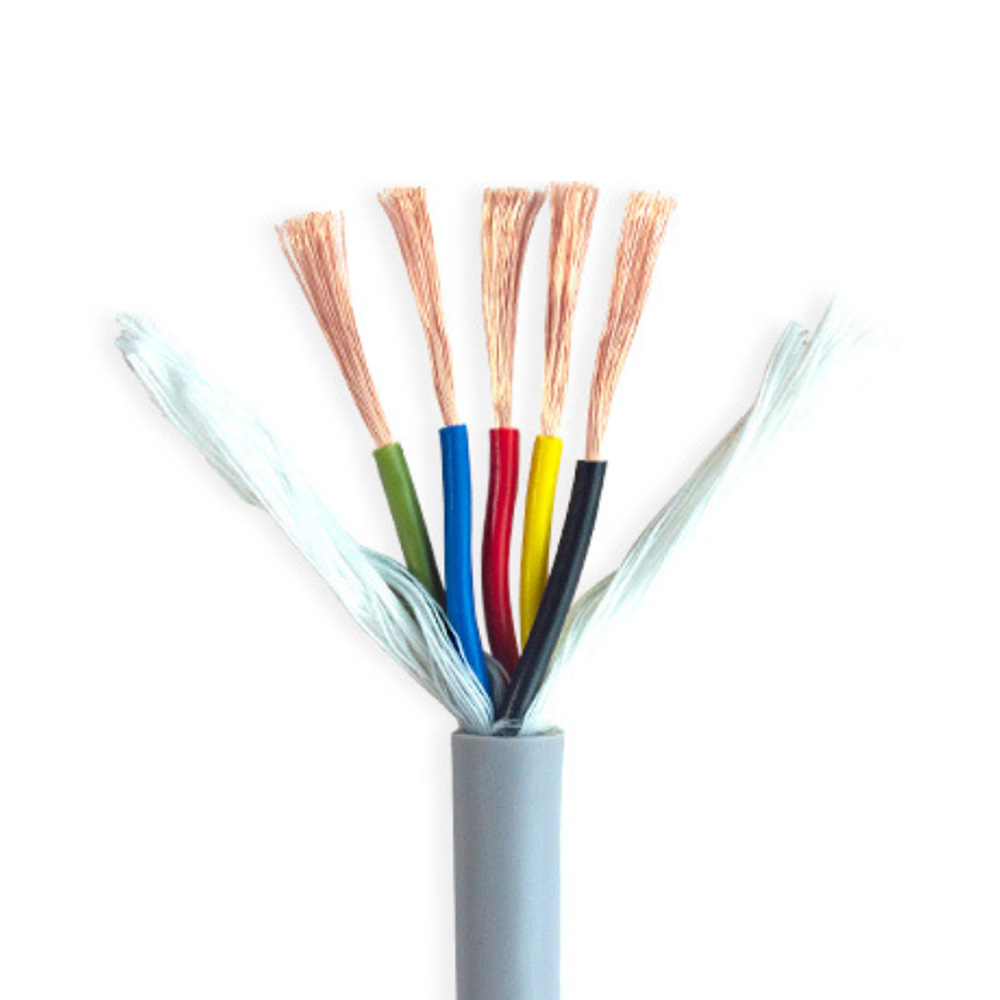
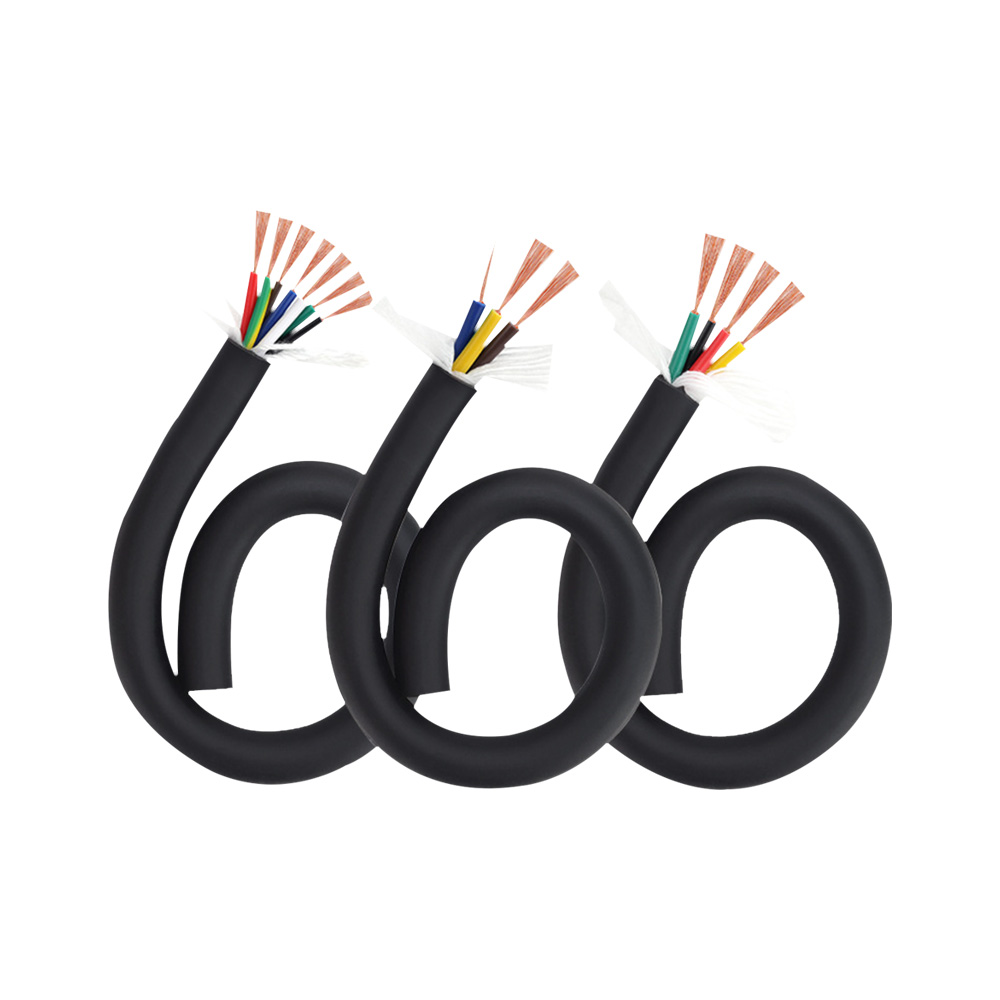
At the heart of the highly flexible energy chain cable lies its exceptional flexibility, a feature achieved through a series of advanced material selections and structural designs. The conductor, typically made of high-purity oxygen-free copper, undergoes a special annealing process that enhances its ductility and fatigue resistance. This allows the conductor to maintain excellent electrical conductivity even after thousands of bending cycles without breaking or losing performance. The insulation layer, on the other hand, is crafted from premium thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) or polyurethane (PU) materials. These materials not only offer superior flexibility but also provide strong resistance to oil, chemicals, high and low temperatures, and abrasion. For instance, high-quality PU insulation can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 80°C, ensuring stable operation in harsh industrial environments such as cold storage facilities or high-temperature manufacturing workshops.
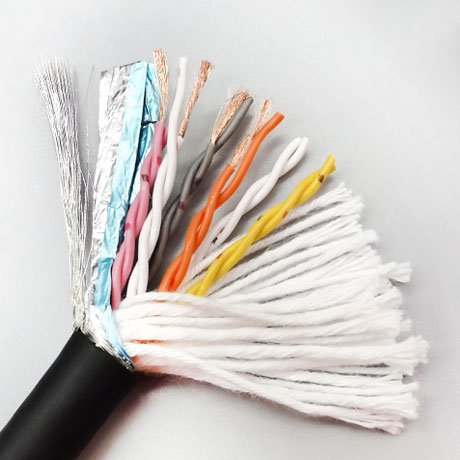
In addition to flexibility, the structural design of the highly flexible energy chain cable is optimized to maximize its service life and reliability. The cable core is often arranged in a stranded or bundled structure, which reduces internal stress during bending and prevents the conductors from tangling or breaking. A reinforced braided shield, made of tinned copper or aluminum-magnesium alloy, is also integrated into the cable structure to provide effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. This is crucial for industrial applications that rely on precise signal transmission, such as CNC machine tools and robotic arms, as it ensures that the cable can operate without being affected by external electrical noise.
The highly flexible energy chain cable is widely used in a variety of industrial sectors, each with its unique requirements and challenges. In the automotive manufacturing industry, for example, the cable is used in robotic welding arms and automated assembly lines, where it must withstand high temperatures, oil splatters, and frequent bending. In the packaging and printing industry, the cable is employed in conveyor systems and printing machines, requiring it to be resistant to abrasion and chemicals from inks and adhesives. In the logistics and material handling sector, the cable powers automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and sorting systems, demanding high flexibility and durability to keep up with the constant movement of the equipment.
One of the key advantages of the highly flexible energy chain cable is its long service life, which helps to reduce maintenance costs and downtime for industrial equipment. Traditional cables often fail after a few thousand bending cycles, leading to unexpected equipment breakdowns and costly repairs. In contrast, a high-quality highly flexible energy chain cable can withstand up to 10 million bending cycles or more, depending on the application and operating conditions. This extended service life is a result of the cable's robust construction and high-quality materials, which ensure that it can endure the rigors of continuous motion without compromising performance.
Another important feature of the highly flexible energy chain cable is its compliance with international industry standards, ensuring that it meets the strict requirements of different markets and applications. For example, many cables are certified by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Underwriters Laboratories (UL), guaranteeing their safety, reliability, and performance. These certifications also make it easier for manufacturers to integrate the cable into their equipment and sell their products in global markets, as they can be confident that the cable meets the necessary regulatory requirements.
When selecting a highly flexible energy chain cable, it is essential to consider the specific needs of the application. Factors such as the number of bending cycles required, the operating temperature range, the type of environment (e.g., oily, dusty, or corrosive), and the level of EMI shielding needed should all be taken into account. Additionally, the cable's electrical parameters, such as voltage rating, current capacity, and signal transmission speed, must match the requirements of the equipment to ensure optimal performance. Working with a reputable cable manufacturer can help to ensure that the selected cable is tailored to the specific application, providing the best possible solution for the customer's needs.
In conclusion, the highly flexible energy chain cable is a critical component in modern industrial automation, enabling the stable and reliable operation of dynamic equipment. Its exceptional flexibility, durability, and resistance to harsh environments make it an ideal choice for a wide range of industrial applications, from automotive manufacturing to logistics and material handling. With its long service life, compliance with international standards, and ability to meet the unique needs of different applications, the highly flexible energy chain cable is poised to play an even more important role in the future of industrial automation, as manufacturers continue to pursue higher levels of efficiency, precision, and reliability in their operations.
FAQs
Common causes of flexible cable failure include:
Over-Bending: Bending the cable beyond its minimum bend radius (MBR) damages conductors and insulation. Prevention: Adhere to the manufacturer’s MBR specifications and use cable management tools (e.g., cable tracks) to control bending paths.
Abrasion & Wear: Friction with surrounding components wears down the sheath. Prevention: Choose cables with wear-resistant sheathing (e.g., PUR) and install protective conduits or cable carriers.
Environmental Damage: Exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures degrades materials. Prevention: Select cables rated for the specific environment and use sealing or shielding where necessary.
Incorrect Installation: Tension, kinking, or improper grounding can strain the cable. Prevention: Follow installation guidelines, avoid pulling cables tightly, and ensure proper grounding for shielded cables.
Eelecting the appropriate flexible cable requires considering several key factors:
Movement Type: Determine if the cable will undergo bending (single or multi-axis), twisting, or torsional movement—this dictates the required flexibility (e.g., high-flex for robotic arms vs. medium-flex for simple folding applications).
Environmental Conditions: Assess temperature range (from extreme cold to high heat), exposure to chemicals, oil, water, or UV radiation—choose insulation/sheathing materials (e.g., PUR for oil resistance, TPE for wide temperature tolerance) accordingly.
Electrical Requirements: Confirm voltage rating, current capacity, and signal transmission needs (e.g., shielded flexible cables for reducing electromagnetic interference in data applications).
Mechanical Durability: Evaluate the number of bending cycles required (e.g., millions of cycles for long-life industrial use) to select cables with suitable conductor stranding and sheath thickness.
lexible cables are widely used in industries and equipment where frequent movement is involved. Common applications include:
Industrial Automation: Robotic arms, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and linear motion systems.
Material Handling: Conveyor belts, hoists, and cranes that require cables to bend with mechanical movement.
Medical Equipment: Portable devices (e.g., ultrasound machines), surgical robots, and patient monitors that need flexible wiring for mobility.
Consumer Electronics: Laptop power cords, headphones, and wearable devices where flexibility ensures user comfort and product longevity.
Automotive Industry: Wiring for folding side mirrors, seat adjustments, and retractable door handles.
A flexible cable is a type of electrical cable designed to withstand repeated bending, twisting, and movement without compromising its electrical performance or structural integrity. Unlike standard fixed-installation cables, which are engineered for static or minimal-movement applications, flexible cables feature specialized constructions—such as fine-stranded conductors (instead of solid or coarse-stranded ones), flexible insulation materials (like PVC, TPE, or PUR), and robust sheathing—that enhance their durability under dynamic stress. This design allows them to be used in scenarios requiring constant motion, such as robotic arms, conveyor systems, and portable equipment.
In industrial scenarios where dynamic motion and signal integrity coexist, standard cables often fail to meet requirements—either lacking flexibility for long-term bending or failing to block interference for precise signals. TRVVPS Twisted Pair Shielded Drag Chain Cable solves these pain points through its integrated design of twisted pairs, shielding, and high flexibility, ensuring reliable, stable, and long-lasting performance. It is a critical cabling solution for upgrading automation levels and improving production precision in modern manufacturing.