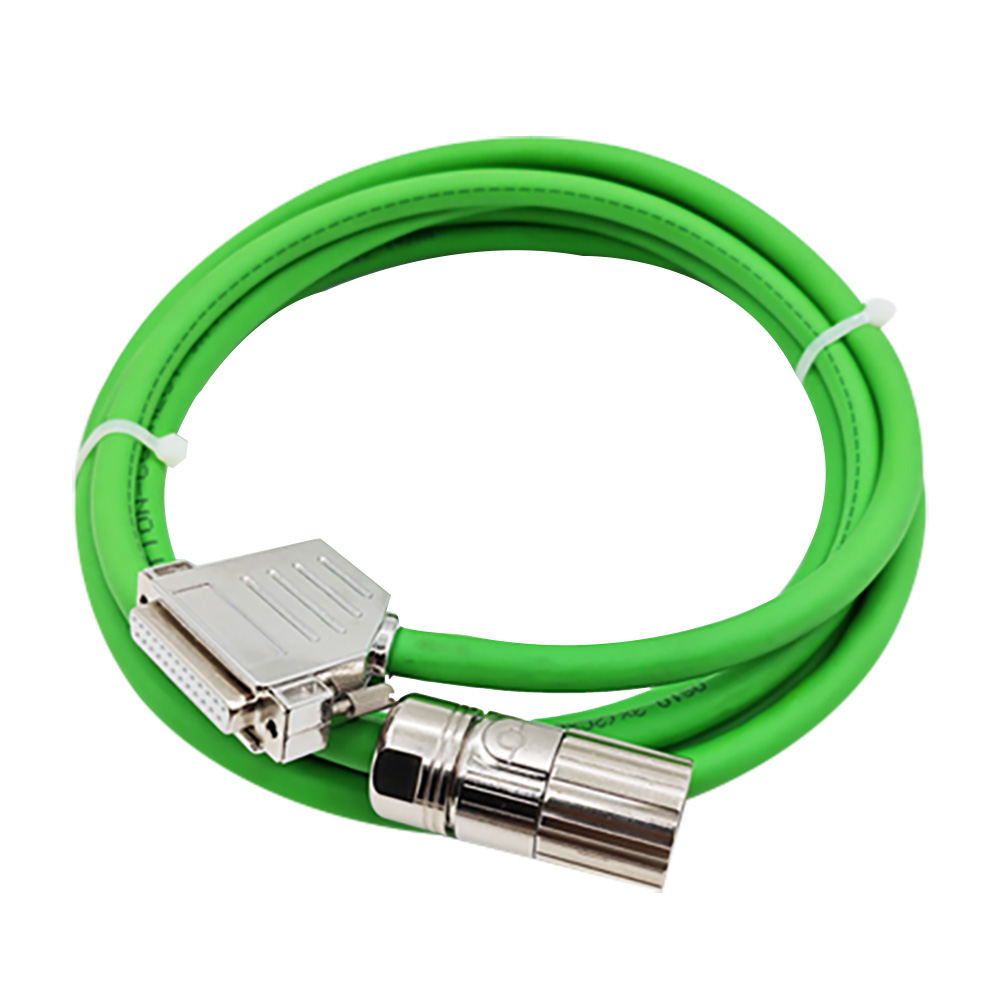
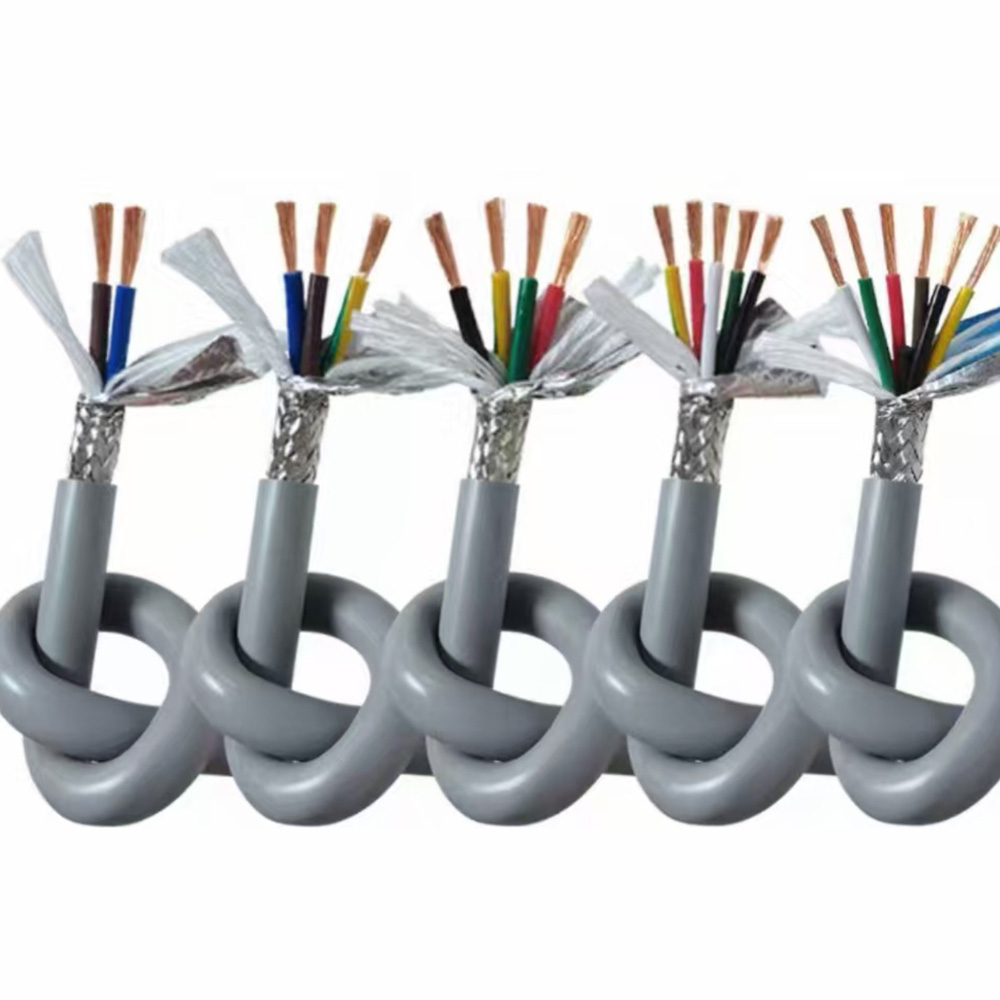
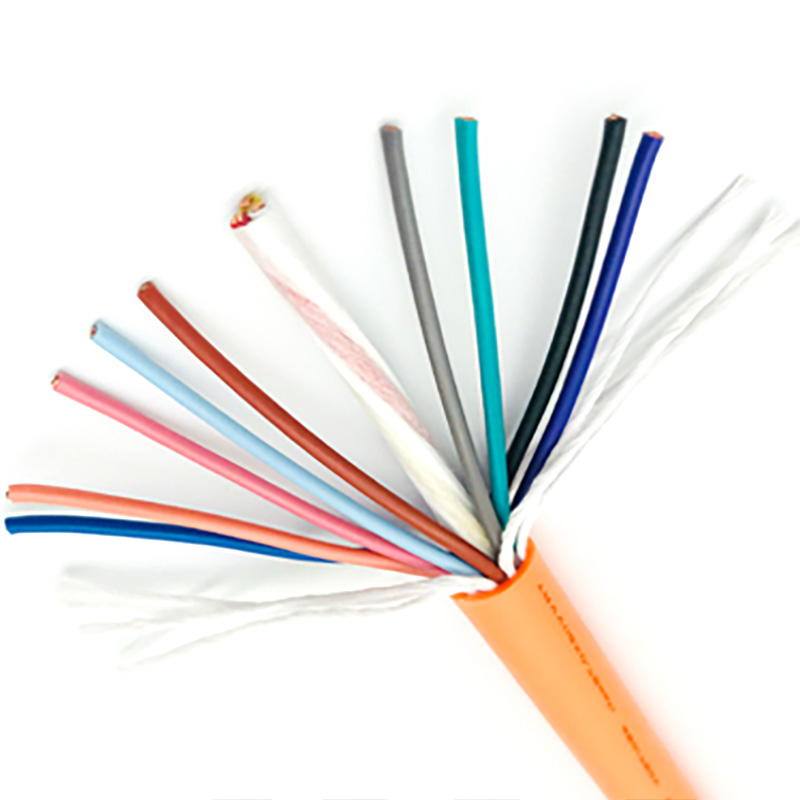
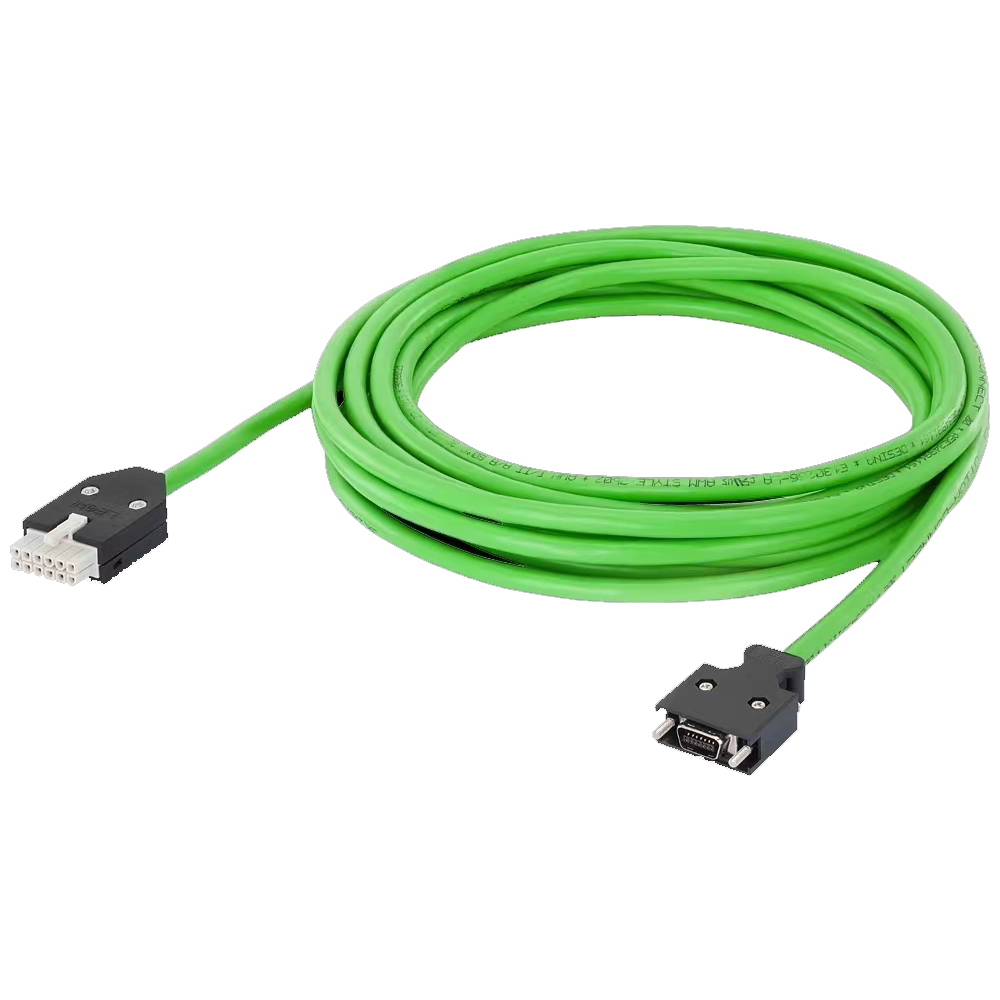
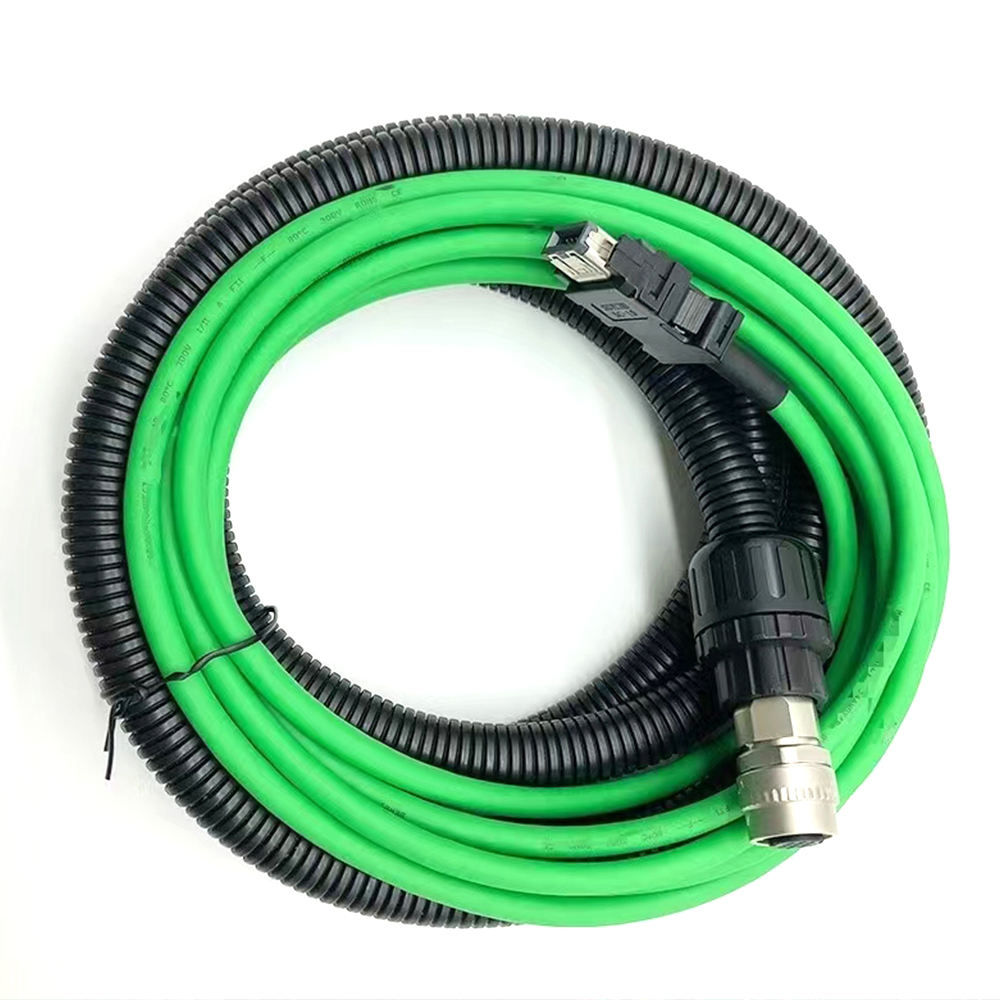
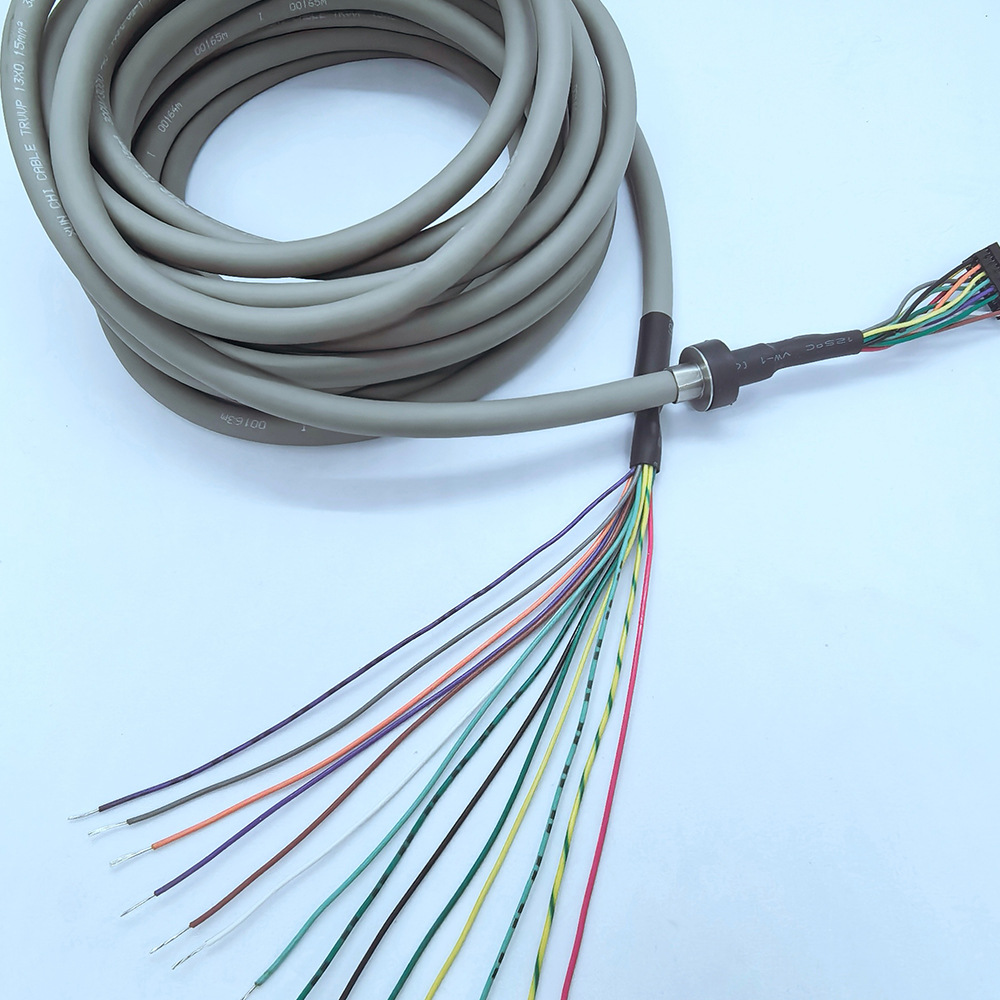
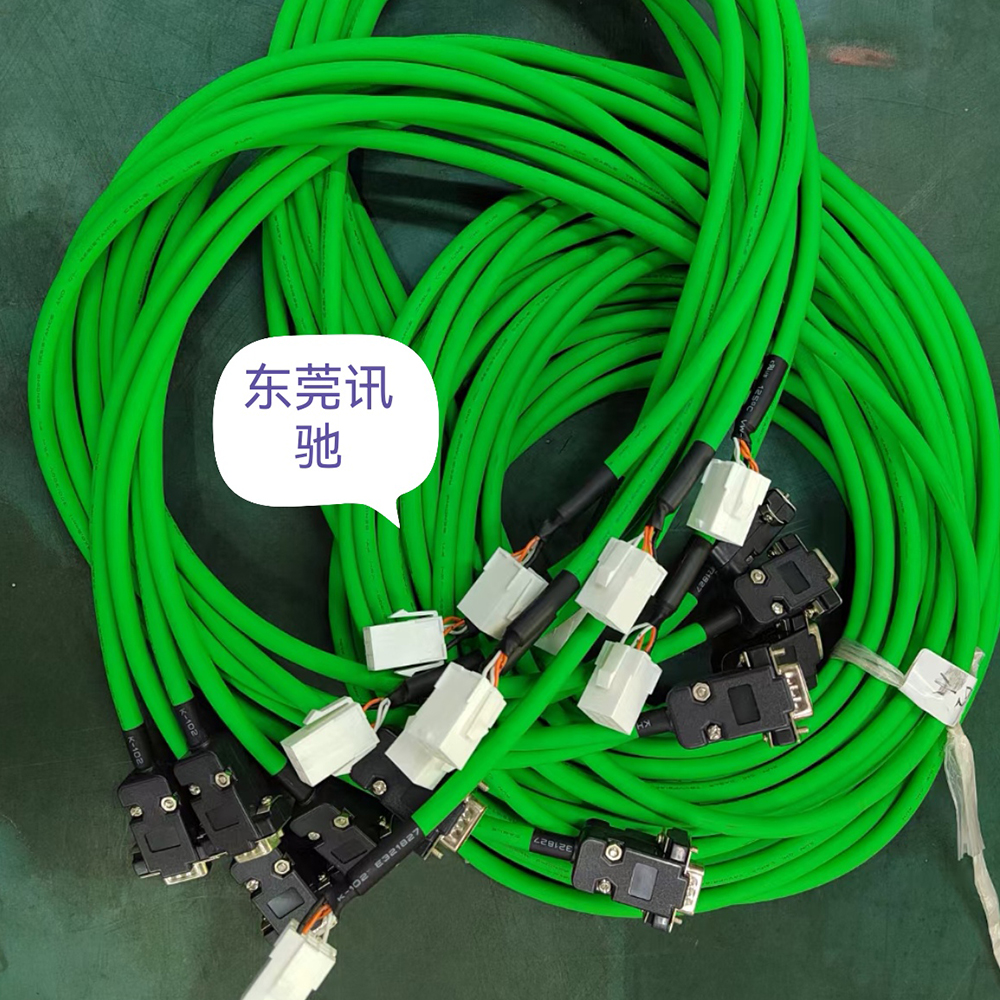
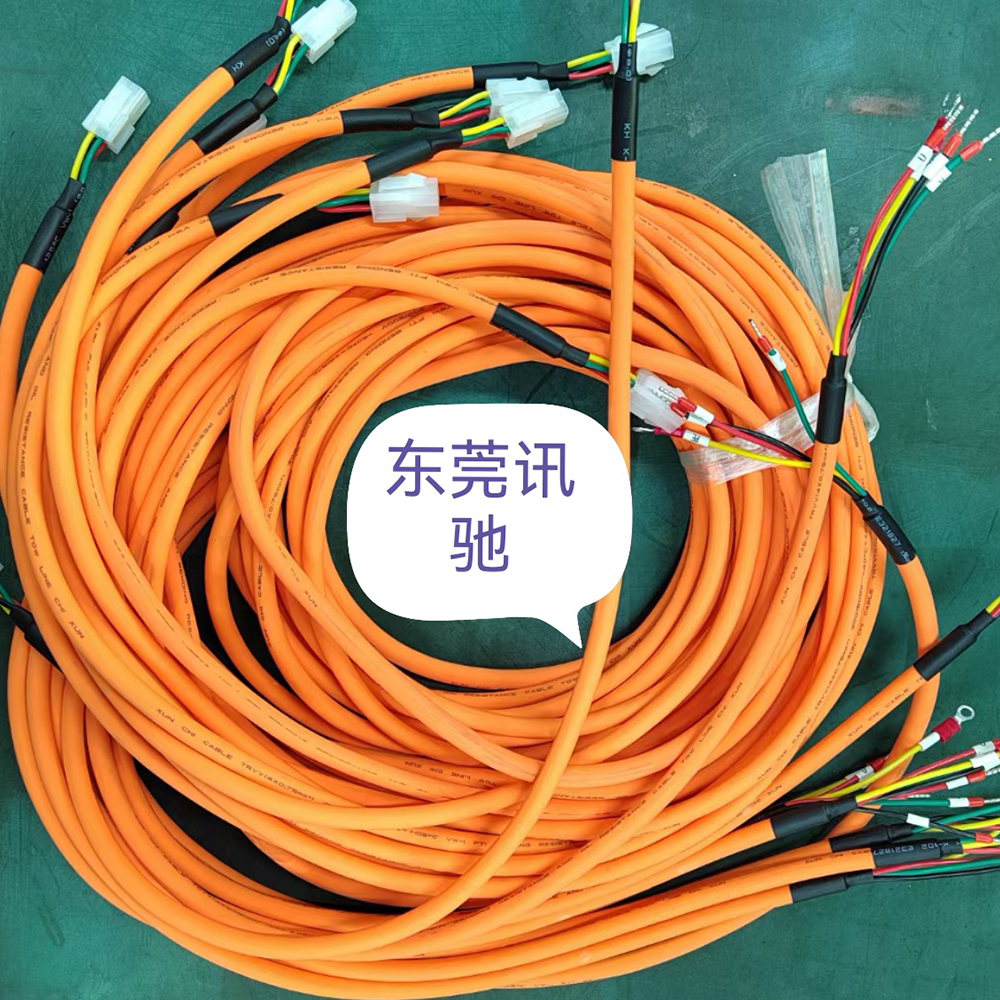
Energy Chain Cable
Energy Chain Cable
- Product Brief: Differences Between Flexible TRVV Drag Chain Cable and Ordinary RVV CableFlexible TRVV drag chain cable refers to a flexible cable that can be used in back moving and bending scenarios in conventional industrial environments. RVV cable, on the other hand, refers to a copper-core polyvinyl chloride i
Description
Differences Between Flexible TRVV Drag Chain Cable and Ordinary RVV CableFlexible TRVV drag chain cable refers to a flexible cable that can be used in back moving and bending scenarios in conventional industrial environments. RVV cable, on the other hand, refers to a copper-core polyvinyl chloride insulated and polyvinyl chloride sheathed flexible wire, which is a type of sheathed wire. From the names of the cables, both have the characteristics of "flexibility" and "softness", so where are the differences between them? And how should we choose during use?
 From the perspective of installation and use, flexible TRVV drag chain cable is mainly suitable for installation and use under continuous reciprocating motion, especially for high-frequency mobile installation in humid or dry scenarios in conventional industrial environments, such as: CNC machine tools, automation equipment, drag chains of modern mechanical standard components, as well as logistics systems, control systems, mechanical automation systems, mechanical (human) hands, construction machinery, heavy machinery factories, automobile manufacturing, lifting and transportation equipment, automated warehouses, docks, fire trucks and other mechanical equipment and scenarios that require high-frequency moving and bending. RVV cable is applied to fixed installation in indoor environments or installation under occasional motion without strong stress relief or forced guidance, such as: power lines, control lines and signal transmission lines for electrical appliances, instruments, electronic equipment and automation devices, and can be specifically used in anti-theft alarm systems, building intercom systems, etc.
From the perspective of installation and use, flexible TRVV drag chain cable is mainly suitable for installation and use under continuous reciprocating motion, especially for high-frequency mobile installation in humid or dry scenarios in conventional industrial environments, such as: CNC machine tools, automation equipment, drag chains of modern mechanical standard components, as well as logistics systems, control systems, mechanical automation systems, mechanical (human) hands, construction machinery, heavy machinery factories, automobile manufacturing, lifting and transportation equipment, automated warehouses, docks, fire trucks and other mechanical equipment and scenarios that require high-frequency moving and bending. RVV cable is applied to fixed installation in indoor environments or installation under occasional motion without strong stress relief or forced guidance, such as: power lines, control lines and signal transmission lines for electrical appliances, instruments, electronic equipment and automation devices, and can be specifically used in anti-theft alarm systems, building intercom systems, etc.
The differences in the use of these two types of cables are mainly caused by their manufacturing processes. Generally speaking, RVV cable consists of two or more RV wires with an additional layer of sheath. The number of its core wires is variable, with two or more, and it has a PVC sheath outside. There are no special requirements for the arrangement between the core wires. For flexible TRVV drag chain cable, there are strict requirements in cable design and core wire structure. The main differences are as follows:
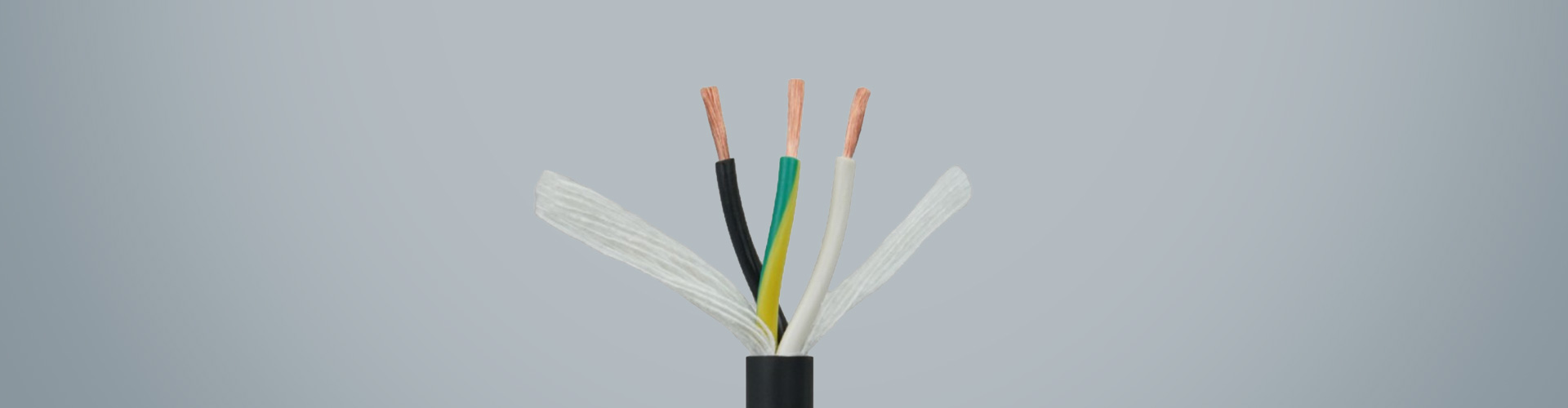
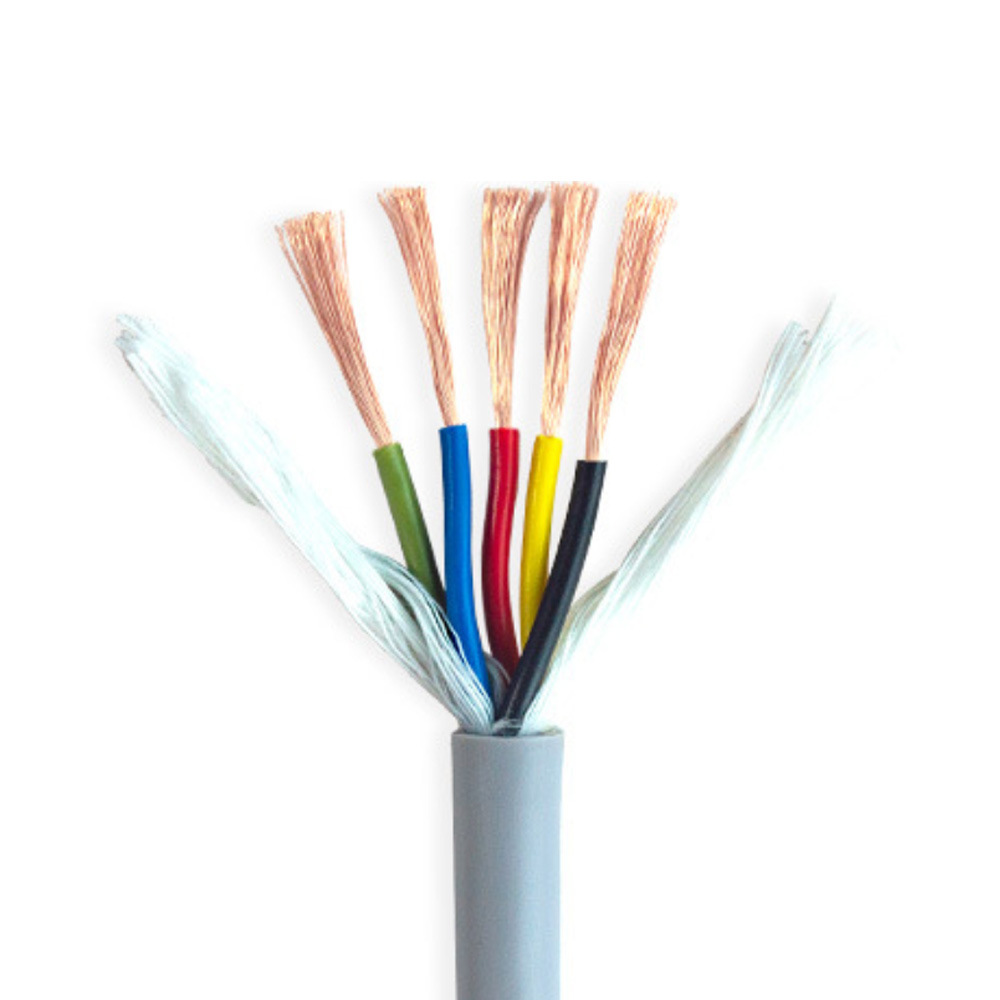
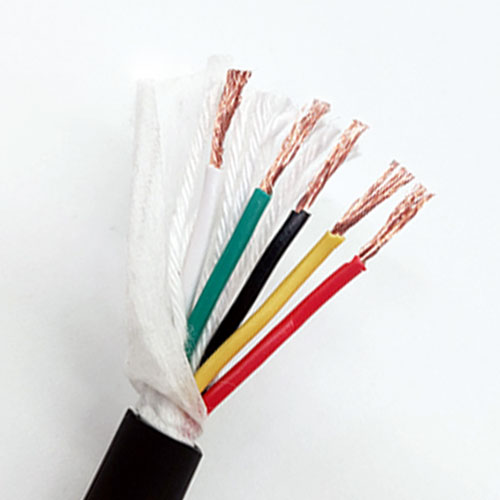
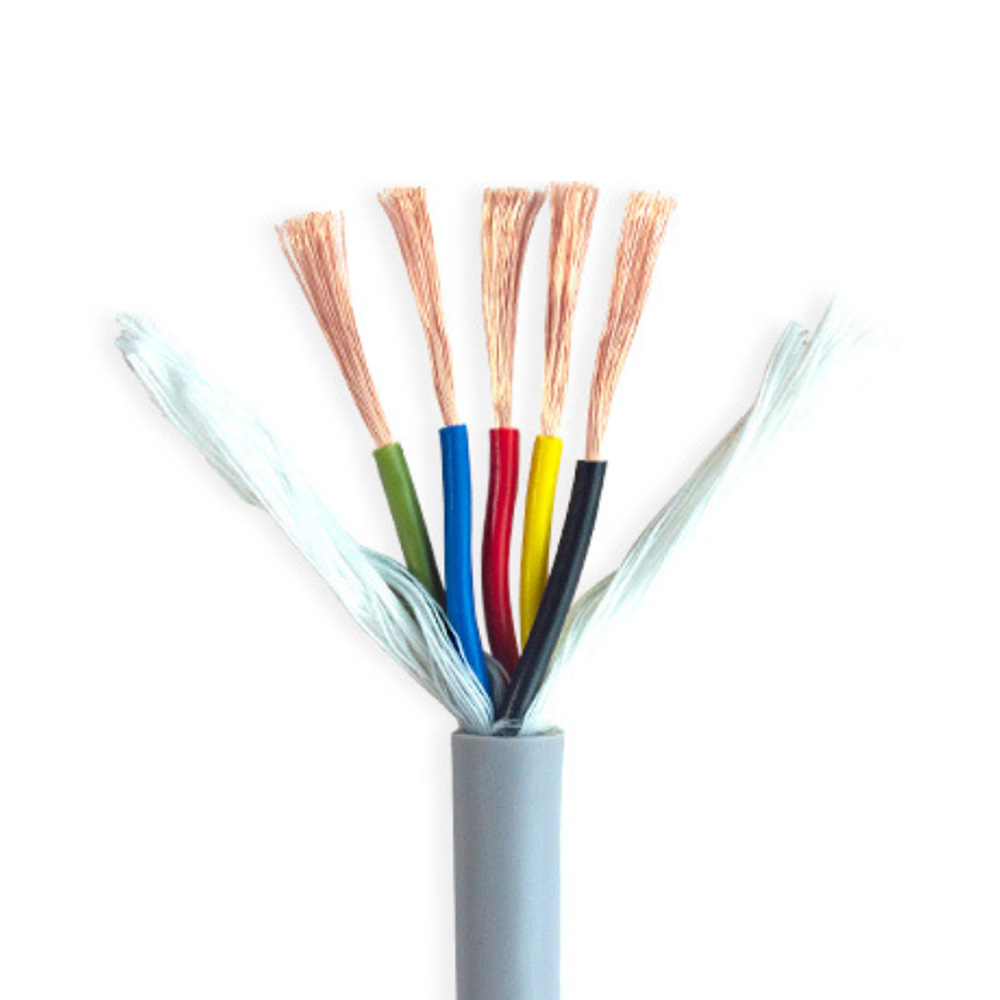
1. **Conductor**: The conductor commonly used in flexible TRVV drag chain cable is generally made of multi-strand oxygen-free copper wires with diameters of 0.08/0.14/0.19mm, which are finely twisted (conductors of large cross-sectional area drag chain cables will also adopt special grouped twisting to ensure that the cable conductors do not break or shift during bending use). The conductor of RVV cable is generally made of oxygen-free copper wires with diameters of 0.2/0.25mm, which are finely calibrated. From the perspective of conductors, TRVV drag chain cable has better flexibility. 2. **Insulation**: The conductor insulation of flexible TRVV drag chain cable generally uses specially modified elastomer materials such as nitrile rubber, automotive-grade materials, TPE, PE, etc. Different insulation materials are selected according to different usage environments to ensure the flexibility of the cable while improving the performance of the cable in specific usage environments to a greater extent. The insulation material of RVV cable is generally ordinary PVC material.
3. **Filling**: Flexible TRVV drag chain cable can be filled with different tensile components such as Kevlar fibers according to the usage environment. While ensuring the cable has a round appearance, it maximizes the performance of the cable in specific scenarios. RVV cable is generally filled with ordinary cable filler to ensure the cable has a round appearance.
4. **Sheath**: Flexible TRVV drag chain cable generally uses specially modified elastomeric nitrile rubber as the sheath material. This kind of cable sheath has basic properties such as flexibility, wear resistance, weather resistance, and tear resistance. RVV cable generally uses ordinary PVC material as the sheath, and its performance is somewhat different from the sheath material used in TRVV drag chain cable. In summary, flexible TRVV drag chain cable has basic properties such as flexibility, wear resistance, bending resistance, tensile resistance (customizable), weather resistance, and tear resistance. It is mainly suitable for high-frequency mobile installation in humid or dry scenarios in conventional industrial environments. It belongs to flexible special mobile cable and can also be specially customized according to different usage environments. RVV cable is more suitable for fixed installation.
FAQs
Common causes of flexible cable failure include:
Over-Bending: Bending the cable beyond its minimum bend radius (MBR) damages conductors and insulation. Prevention: Adhere to the manufacturer’s MBR specifications and use cable management tools (e.g., cable tracks) to control bending paths.
Abrasion & Wear: Friction with surrounding components wears down the sheath. Prevention: Choose cables with wear-resistant sheathing (e.g., PUR) and install protective conduits or cable carriers.
Environmental Damage: Exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures degrades materials. Prevention: Select cables rated for the specific environment and use sealing or shielding where necessary.
Incorrect Installation: Tension, kinking, or improper grounding can strain the cable. Prevention: Follow installation guidelines, avoid pulling cables tightly, and ensure proper grounding for shielded cables.
Eelecting the appropriate flexible cable requires considering several key factors:
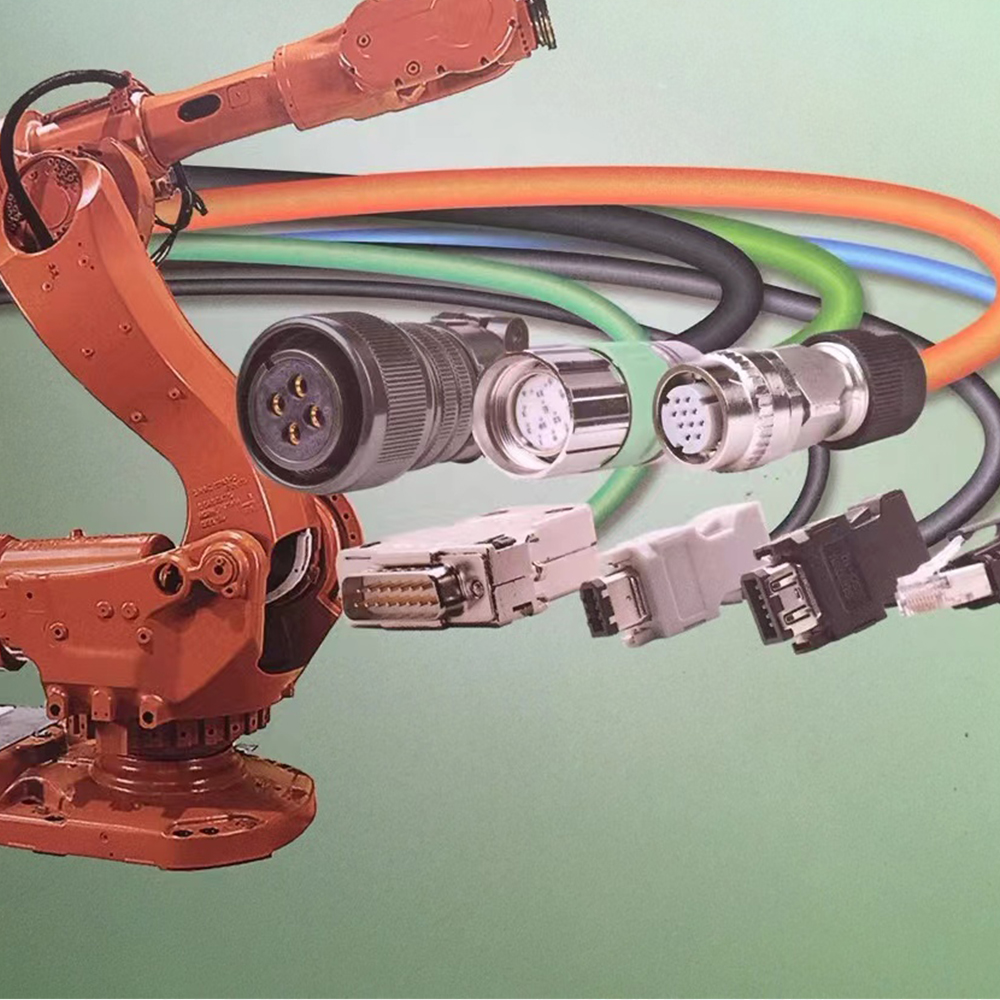
Movement Type: Determine if the cable will undergo bending (single or multi-axis), twisting, or torsional movement—this dictates the required flexibility (e.g., high-flex for robotic arms vs. medium-flex for simple folding applications).
Environmental Conditions: Assess temperature range (from extreme cold to high heat), exposure to chemicals, oil, water, or UV radiation—choose insulation/sheathing materials (e.g., PUR for oil resistance, TPE for wide temperature tolerance) accordingly.
Electrical Requirements: Confirm voltage rating, current capacity, and signal transmission needs (e.g., shielded flexible cables for reducing electromagnetic interference in data applications).
Mechanical Durability: Evaluate the number of bending cycles required (e.g., millions of cycles for long-life industrial use) to select cables with suitable conductor stranding and sheath thickness.
lexible cables are widely used in industries and equipment where frequent movement is involved. Common applications include:
Industrial Automation: Robotic arms, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and linear motion systems.
Material Handling: Conveyor belts, hoists, and cranes that require cables to bend with mechanical movement.
Medical Equipment: Portable devices (e.g., ultrasound machines), surgical robots, and patient monitors that need flexible wiring for mobility.
Consumer Electronics: Laptop power cords, headphones, and wearable devices where flexibility ensures user comfort and product longevity.
Automotive Industry: Wiring for folding side mirrors, seat adjustments, and retractable door handles.
A flexible cable is a type of electrical cable designed to withstand repeated bending, twisting, and movement without compromising its electrical performance or structural integrity. Unlike standard fixed-installation cables, which are engineered for static or minimal-movement applications, flexible cables feature specialized constructions—such as fine-stranded conductors (instead of solid or coarse-stranded ones), flexible insulation materials (like PVC, TPE, or PUR), and robust sheathing—that enhance their durability under dynamic stress. This design allows them to be used in scenarios requiring constant motion, such as robotic arms, conveyor systems, and portable equipment.
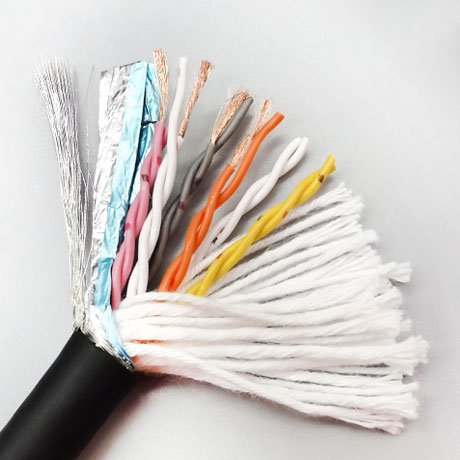
In industrial scenarios where dynamic motion and signal integrity coexist, standard cables often fail to meet requirements—either lacking flexibility for long-term bending or failing to block interference for precise signals. TRVVPS Twisted Pair Shielded Drag Chain Cable solves these pain points through its integrated design of twisted pairs, shielding, and high flexibility, ensuring reliable, stable, and long-lasting performance. It is a critical cabling solution for upgrading automation levels and improving production precision in modern manufacturing.